What is ESG Data and How do you Use it?
ESG data provides information about the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) attributes of a company or investment. ESG data is used by investors, analysts, companies, policymakers, and other stakeholders to understand and make informed decisions about business effectiveness, risk, and sustainability.
ESG data is used in many different ways, including:
- ESG data is used by analysts to rank and determine a company or investment's ESG score or rating
- ESG data is used by investors to assess an investment's ESG risks and opportunities
- Companies use ESG data for a variety of reasons, including internal performance tracking, supplier evaluations, and corporate ESG reporting
For companies, collecting, tracking, and reporting ESG data is a key step to establish transparency, trust, and accountability around their environmental goals, social sustainability, and corporate governance so they can appeal to investors, employees, and customers - while also staying compliant with relevant ESG regulations.
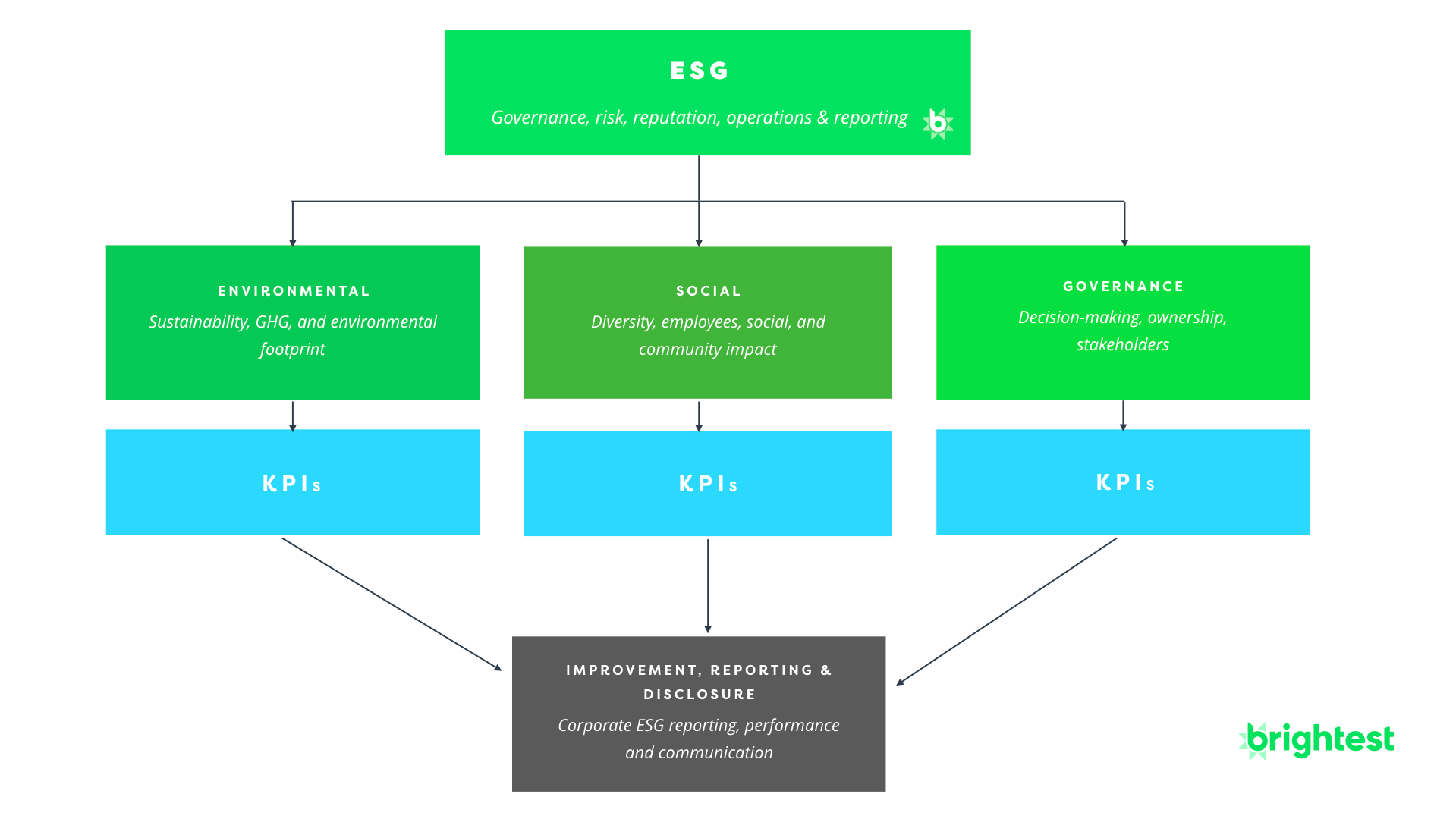
Types of ESG Data
ESG data refers to information related to a company's environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. The different types of ESG data can be broadly categorized into the following areas:
- Environmental data: This includes data on a company's energy usage, carbon emissions, water usage, and waste management practices
- Social data: This includes data on a company's labor practices, human rights policies, community engagement, and diversity and inclusion initiatives
- Governance data: This includes data on a company's board composition, executive pay, anti-corruption policies, and other metrics
- Financial data: This includes the financial performance and stability of the company, which may be used alongside other ESG data to calculate intensity ratios and other ESG KPIs
There are many different methodologies used to collect and analyze ESG data, including investment incides and ratings from MSCI and S&P, as well as ESG data collection platforms for companies like Brightest.
The Benefits of Better ESG Data
Quality ESG data provides a number of benefits for companies, investors, and other stakeholders. Some of the key benefits of ESG data include:
- Risk management: ESG data can help companies identify and mitigate potential environmental and social risks that could impact their operations, value chain, and reputation. This can also help investors identify companies that may be exposed to risks such as climate change, labor disputes, or human rights violations
- Long-term performance: Companies that prioritize and manage ESG issues may be better positioned for long-term success and shareholder value creation. Studies have shown that companies with strong ESG performance tend to have better financial results, lower market volatility, and are more resilient to market downturns
- Reputation and brand: ESG data can help companies communicate their commitment to sustainability and social responsibility to stakeholders. This can enhance their reputation, build trust, and attract customers and employees who value these issues
- Increased investor interest: There is growing interest among investors in incorporating ESG factors into their investment decisions. As a result, companies that prioritize and manage ESG issues may have access to a broader range of investors and potentially at a better valuation
- Compliance: ESG data can help companies comply with regulations and international agreements related to environmental and social issues
- Hiring, recruiting, and employee retention: ESG data and disclosure helps demonstrating a company's commitment to ethical practices, employee well-being, and social responsibility. Research shows this often translates to increased employee loyalty, higher levels of engagement, better recruiting outcomes, and improved productivity.
- Improved business decision-making: ESG data provides companies with a more comprehensive view of their operations and can inform decisions around strategy, operations, risks, opportunities, and investments
A number of researchers, analysts, and companies like Campbell's, Havas, Nike, Starbucks, TIAA, and Unilever have all found clear correlations between robust ESG programs and employee morale, loyalty, and retention, and - in some cases - direct sales growth. Understanding those relationships require strong ESG data foundations, infrastructure, and analytics capabilities.
These benefits make it important for companies to accurately collect, management, and disclose ESG data, particularly publicly-traded or listed organizations.
ESG Data in ESG Ratings and Analyst Scoring
ESG data is commonly used to calculate ESG scores and ratings that can be used to evaluate a company's performance on environmental, social, and governance issues. There are different methodologies, frameworks, and types of data used to determine ESG scores and ratings, but the basic process generally follows this type of pattern:
- ESG data collection: ESG data is collected from various sources, such as corporate ESG reports, news articles, and government data. Some organizations use standardized data collection frameworks, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or Task Force for Climate-Related Financial Disclosure (TCFD), to ensure consistency and comparability across companies
- ESG data analysis: The collected ESG data is analyzed and evaluated to determine a company's performance on ESG issues compared to industry benchmarks. This often involves assigning a score or rating for each area of an organization or investment's ESG performance, such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices
- Weighting and aggregation: Scores or ratings for each area of ESG performance are often weighted and aggregated to produce an overall ESG score or rating for a company. The weighting of the different areas of ESG performance can vary depending on the organization or framework used
- Benchmarking and comparison: Overall ESG scores and ratings are often compared against peer or industry standard ESG data benchmarks to compare across companies. Some organizations also provide a ESG score or rating for the sector or industry as a whole
It's important to note that different organizations, analysts, investors, and agencies use different methodologies and weighting to calculate ESG scores and ratings, so scores - and the underlying ESG data used - can vary depending on the provider. Some organizations also use different ESG data sources, therefore the scores and ratings can vary based on what data's used. Most leading ESG analysts publish their methodology on what data they collect and how it's used.
Collecting ESG Data Within Companies
Most large, international companies have internal teams and processes to collect ESG data. This includes:
- What ESG data does the business currently track or plan to track in the future?
- Where does that data currently live? Is there an HR system that stores ESG social data? Is there a facilities or financial system that contains important environmental data?
- How are sustainability and ESG data collected? Who is responsible for different aspects of data collection? What processes are followed?
- When is ESG data collected? In real-time? Monthly? Quarterly? Annually? It may be different for different departments, regions, and metrics
For example, its common for ESG, sustainability, and finance teams to collect and gather environmental ESG data from accounting, operations, and/or facilities, social data from HR, and governance data from the board, finance, legal, risk, and other parts of the organization. ESG data collection and management may require onboarding an ESG data management system like Brightest, and coordinating that with IT and procurement. Support from consultants may also be needed. ESG data collection is truly an aggregation process, one that requires significant cross-organizational collaboration, communication, and stakeholder engagement.
Need a unified system to collect, track, and report your ESG data?
Brightest helps hundreds of companies around the world prioritize, manage, measure, report, and improve their ESG data collection, accuracy, and insights
While individual departments may be responsible for specific ESG metrics and measurement areas, it's important for CEOs, CFOs, and sustainability leaders to create a unified, company-wide ESG data and analytics approach. In order for ESG to really drive business benefits, competitive advantages, and social impact, it must be part of the company's top-level strategy, supported by the C-suite, and informing decisions across the organization.
You can't delegate ESG or sustainability to a single department - it's a company-wide effort
Similarly, rather than trying collect data on everything, it's best to focus ESG data efforts on accuracy, controls, data quality, and measuring a few core ESG and sustainability KPIs first, then building from there.
There are several steps and best practices any company can follow to effectively collect operational sustainability and ESG data:
- Start with the most important and relevant ESG data: It's important to focus on a company's most important and material ESG data. This includes leading ESG metrics like energy usage, Scope 1, 2 & 3 emissions, and employee diversity
- Determine the primary sources of ESG data: Is ESG data in IT systems? Spreadsheets? PDFs and documents? Third party data sources and benchmarks? All of the above? Determine what processes are needed to safely and accurately collect and centralize all these documents and data (particularly from an audit perspective)
- Engage and educate ESG data stakeholders: It's important to build buy-in with ESG data collectors and collaborators. Do they understand how to collect the data that's needed? Do they understand how to efficiently share it? Do they understand why this matters and how it ties into the company's overall strategy?
- Establish processes for collecting and storing ESG data: To ensure ESG data is accurate and auditable, it's important to establish clear processes, schedules, and accountability for collecting, reviewing, and storing it. This should involve designating specific individuals or teams to be responsible for collecting and organizing specific ESG data, setting up systems for centrally storing the data, establishing data quality checks and data hygeine standards, and establishing worklows and processes for audit and data review
- Considering ESG data outputs: Once ESG data is collected, centralized, and being managed effectively, what are they key outputs and usage areas? This typically includes an annual ESG or sustainability report, ESG survey and questionnaire responses, as well as internal business intelligence processes and systems to inform data analysis
A good ESG data collection system should be able to gather data across a company's operations, supply chain, disclosures, third-party data providers, and publicly available information. The system should also be able to organize and analyze the data in a way that is meaningful and useful for stakeholders, such as investors, customers, and employees.
In many cases, implementing ESG data collection improvements will require organizational change management. Above all, organizational alignment, resourcing, and executive support are critical for efficient, effective, long-term ESG data collection success.
ESG Data Partners and Providers
ESG data partners like suppliers, third party experts, consultants, independent standards organizations, industry associations, or ESG technology providers like Brightest can often provide helpful best practices when it comes to collecting and working with ESG data.

Brightest helps collect and centralize ESG data across all of a company's systems, teams, and data sources
There are a variety of reputable ESG data analysts and providers available, including Bloomberg, CDP, ISS, MSCI, Refinitiv, RobecoSAM, S&P, Sustainalytics, Vigeo Eiris, and others. Familiarize yourself with their research, methodology, and offerings to see if their ESG data solutions are a fit for your needs. The ESG data market is also constantly evolving, with new players emerging.
Concluding Thoughts on ESG Data Collection
Effectively understanding, communicating, and working with ESG data is one of the most important responsibilities of any ESG professional. Data underpins overall ESG performance and disclosure.
Overall, ESG data is a vital tool for companies, investors, and other stakeholders to understand and manage environmental, social, and governance issues. By providing insight into a company's performance on ESG issues, ESG data can help to mitigate risks, improve long-term performance, enhance reputation and brand, increase investor interest, and help comply with regulations and international agreements. Our hope is this article served as a helpful initial overview of the different types of ESG data, the benefits of ESG data, and the methodologies and frameworks used to determine ESG scores and ratings. As the importance of ESG data continues to grow, it is essential for companies, investors and other stakeholders to understand and use it to make informed decisions.
With that said, we wish you all the best with your ESG data work and learnings. If we can be helpful at all (at any step in your process), please get in touch. A central part of our mission here at Brightest is empowering more efficient, transparent, and well-governed ESG data.





